Example for Gauss-Newton method
Contents
Define function f(x) and Jacobian f'(x)
Here we use @-functions in Matlab. For more complicated functions one can define the functions in separate m-files f.m and fp.m .
f = @(x) [x(1)-1; x(2)-2 ; x(1)^2+x(2)^2-3]; fp = @(x) [ 1, 0 ; 0, 1; 2*x(1), 2*x(2) ];
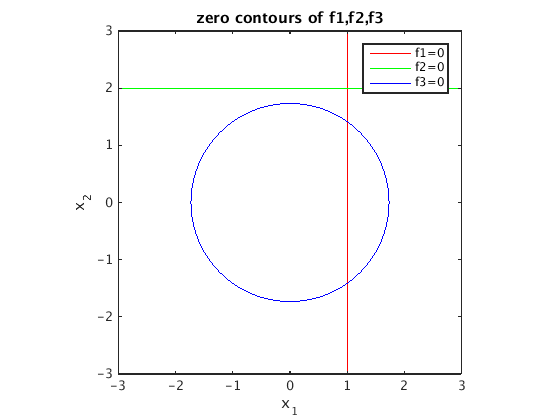
Plot zero contours of the functions f1, f2, f3
h = ezplot('1*x1+0*x2-1',[-3 3 -3 3]); hold on % plot curves where f1=0 set(h,'LineColor','r'); % and make this red h = ezplot('0*x1+1*x2-2',[-3 3 -3 3]); % plot curves where f2=0 set(h,'LineColor','g'); % and make this green h = ezplot('x1^2+x2^2-3',[-3 3 -3 3]); % plot curves where f3=0 set(h,'LineColor','b'); % and make this blue title('zero contours of f1,f2,f3') axis equal legend('f1=0','f2=0','f3=0')
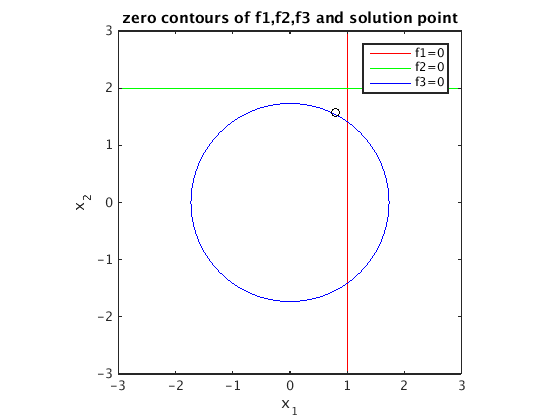
Perform 10 Gauss-Newton steps starting with [0;0]
x = [0;0]; % initial guess for i=1:10 b = f(x); % evaluate f fprintf('x=[%20.17g,%20.17g], ||f(x)||=%20.17g\n',x,norm(b)) A = fp(x); % evaluate Jacobian d = -A\b; % solve norm(A*d+b)=min x = x + d; end plot(x(1),x(2),'ko'); hold off % mark solution point with 'o' title('zero contours of f1,f2,f3 and solution point')
x=[ 0, 0], ||f(x)||= 3.7416573867739409 x=[ 1, 2], ||f(x)||= 2 x=[ 0.80952380952380942, 1.6190476190476191], ||f(x)||= 0.50787576572339488 x=[ 0.79127532704128101, 1.5825506540825622], ||f(x)||= 0.48464618206378557 x=[ 0.79142841595063729, 1.5828568319012746], ||f(x)||= 0.48464457916624887 x=[ 0.79142541916499731, 1.5828508383299948], ||f(x)||= 0.4846445785517931 x=[ 0.79142547754473658, 1.5828509550894729], ||f(x)||= 0.4846445785515599 x=[ 0.79142547640734506, 1.5828509528146903], ||f(x)||= 0.48464457855155979 x=[ 0.79142547642950456, 1.5828509528590089], ||f(x)||= 0.4846445785515599 x=[ 0.79142547642907268, 1.5828509528581454], ||f(x)||= 0.48464457855155973
Find errors
We see that we have convergence of order 1: the error gets multiplied by about .02 with each iteration.
xs = x; % xs is exact solution which we just found x = [0;0]; % initial guess olderr = NaN; for i=1:10 b = f(x); % evaluate f A = fp(x); % evaluate Jacobian d = -A\b; % solve norm(A*d+b)=min x = x + d; err = norm(x-xs); fprintf('||x-xs||=%8.2e, ratio=%g\n',err,err/olderr) olderr = err; end
||x-xs||=4.66e-01, ratio=NaN ||x-xs||=4.05e-02, ratio=0.0867715 ||x-xs||=3.36e-04, ratio=0.00829631 ||x-xs||=6.57e-06, ratio=0.0195773 ||x-xs||=1.28e-07, ratio=0.0194807 ||x-xs||=2.49e-09, ratio=0.0194826 ||x-xs||=4.86e-11, ratio=0.0194828 ||x-xs||=9.46e-13, ratio=0.0194728 ||x-xs||=1.91e-14, ratio=0.0201451 ||x-xs||=0.00e+00, ratio=0