Exam 2
Contents
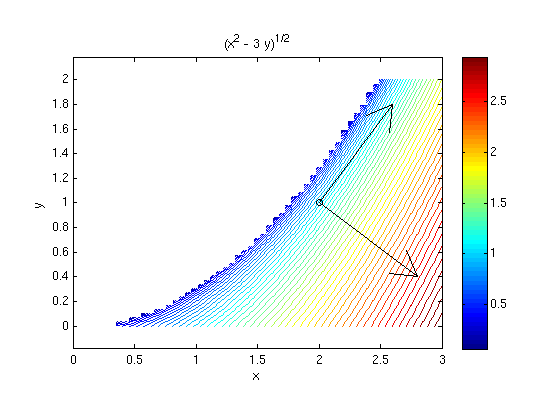
1: Let f(x,y)=sqrt(x^2-3y) and (x0,y0)=(2,1)
First find z0 = f(x0,y0) and g=grad f(x0,y0).
syms x y x0 = 2; y0 = 1; f = sqrt(x^2-3*y); fx = diff(f,x) fy = diff(f,y) z0 = subs(f,{x,y},{x0,y0}) g = subs([fx,fy],{x,y},{x0,y0})
fx = x/(x^2 - 3*y)^(1/2) fy = -3/(2*(x^2 - 3*y)^(1/2)) z0 = 1 g = [ 2, -3/2]
1(a):
Find a unit vector a such that the directional derivative is maximal, give the value of the directional derivative.
amax = g/norm(g) % unit vector in direction of g
dir_deriv = norm(g)
amax = [ 4/5, -3/5] dir_deriv = 5/2
1(b)
Find a unit vector a such that the directional derivative is zero.
a0 = [-g(2),g(1)]/norm(g) % unit vector orthogonal on g ezcontourc(f,[0 3 0 2],51); hold on plotpts([x0,y0],'ko'); arrow([x0,y0],amax,'k'); arrow([x0,y0],a0,'k'); hold off; axis equal; colorbar
a0 = [ 3/5, 4/5]
1(c)
Use the tangent plane approximation to approximate f(1.9,1.2).
p = z0 + dot(g,[1.99,1.02]-[x0,y0]) % evaluate p(x0,y0) double(p) double(subs(f,{x,y},{1.99,1.02})) % f(x0,y0) for comparison
p =
19/20
ans =
0.9500
ans =
0.9487
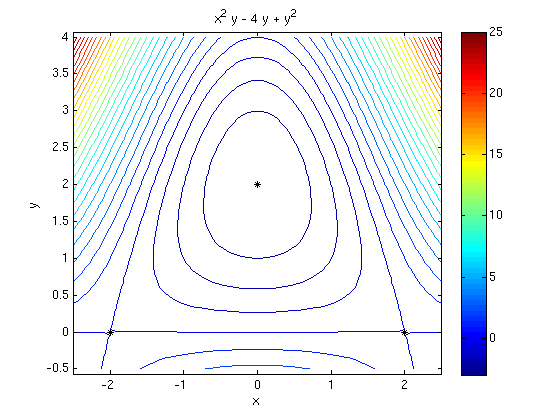
2(a)
Find all critical points of the function f(x,y) = x^2*y + y^2 - 4*y
Answer: Three critical points (2,0) (saddle pt), (0,2) (rel.min.), (-2,0) (saddle pt)
syms x y f = x^2*y + y^2 - 4*y fx = diff(f,x) fy = diff(f,y) fxx = diff(fx,x) fxy=diff(fx,y) fyy=diff(fy,y) D = fxx*fyy-fxy^2; [xs,ys] = solve(fx,fy,x,y); [xs,ys] % find critical points subs([D,fxx],{x,y},{xs,ys}) % evaluate D and fxx in all critical points ezcontourc(f,[-2.5 2.5 -0.5 4],-3:25); colorbar; hold on plotpts([xs,ys],'k*'); hold off; axis equal
f = x^2*y + y^2 - 4*y fx = 2*x*y fy = x^2 + 2*y - 4 fxx = 2*y fxy = 2*x fyy = 2 ans = [ 2, 0] [ 0, 2] [ -2, 0] ans = [ -16, 0] [ 8, 4] [ -16, 0]
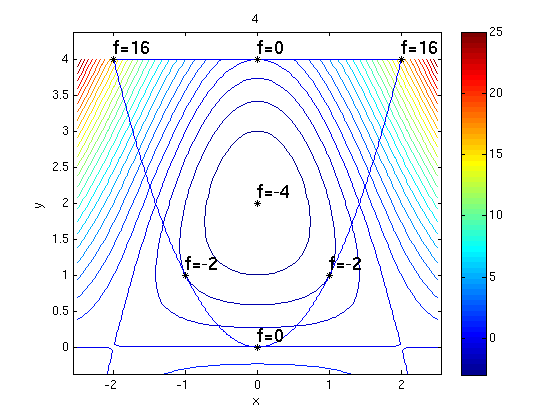
2(b)
xi = 0; yi = 2; % interior critical point from 2(a) g1 = x^2; % y for lower boundary F1 = subs(f,y,x^2) % f on lower boundary F1p = diff(F1,x) xs1 = solve(F1p,x) % critical points on lower boundary ys1 = subs(g1,x,xs1) % corresponding y values g2 = sym(4); % y for upper boundary F2 = subs(f,y,4) % f on upper boundary F2p = diff(F2,x) xs2 = solve(F2p,x) % critical points on upper boundary ys2 = subs(g2,x,xs2) % corresponding y values xc = [-2;2]; yc = [4;4]; % two corner points X = [xi;xs1;xs2;xc]; % list of all points where extrema may occur Y = [yi;ys1;ys2;yc]; Z = subs(f,{x,y},{X,Y}); % show x,y,f(x,y) for all points in list [X,Y,Z] Zd = double(Z); % need to convert to double for min, max fmax = max(Zd) fmin = min(Zd) ezcontourc(f,[-2.5 2.5 -0.5 4],-3:25); colorbar; hold on ezplot(g1,[-2,2]); % draw lower boundary ezplot(g2,[-2,2]); % draw upper boundary plotpts([X,Y],'k*'); % draw all points in list for i=1:length(X) % and label them with 'f=...' texts([X(i),Y(i)],sprintf('f=%g',Zd(i))) end hold off; axis equal
F1 =
2*x^4 - 4*x^2
F1p =
8*x^3 - 8*x
xs1 =
0
1
-1
ys1 =
0
1
1
F2 =
4*x^2
F2p =
8*x
xs2 =
0
ys2 =
4
ans =
[ 0, 2, -4]
[ 0, 0, 0]
[ 1, 1, -2]
[ -1, 1, -2]
[ 0, 4, 0]
[ -2, 4, 16]
[ 2, 4, 16]
fmax =
16
fmin =
-4
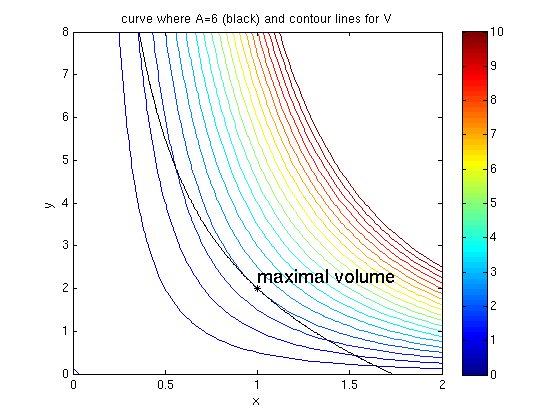
3: Maximize volume of cylinder if surface area = 6*pi.
Answer: Volume is maximal for radius x=1 and height y=2.
syms x y lambda A = 2*x^2 + 2*x*y % surface area is pi*A V = x^2*y % volume is pi*V Ax = diff(A,x) Ay = diff(A,y) Vx = diff(V,x) Vy = diff(V,y) [Vx-lambda*Ax;Vy-lambda*Ay;A-6] s = solve(Vx-lambda*Ax,Vy-lambda*Ay,A-6,x,y,lambda); [s.x,s.y] % two critical points ezcontourc(V,[0 2 0 8],0:.5:10); colorbar; hold on p = ezplot(A-6,[0 2 0 8]); % draw curve where A=6 set(p,'Color','black') plotpts([s.x,s.y],'k*'); texts([s.x(1),s.y(1)],'maximal volume') hold off title('curve where A=6 (black) and contour lines for V')
A =
2*x^2 + 2*y*x
V =
x^2*y
Ax =
4*x + 2*y
Ay =
2*x
Vx =
2*x*y
Vy =
x^2
ans =
2*x*y - lambda*(4*x + 2*y)
x^2 - 2*lambda*x
2*x^2 + 2*y*x - 6
ans =
[ 1, 2]
[ -1, -2]