Examples: Surface area
Contents
(1): Surface area of paraboloid
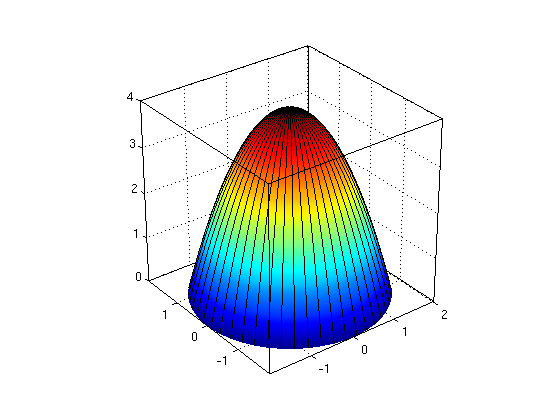
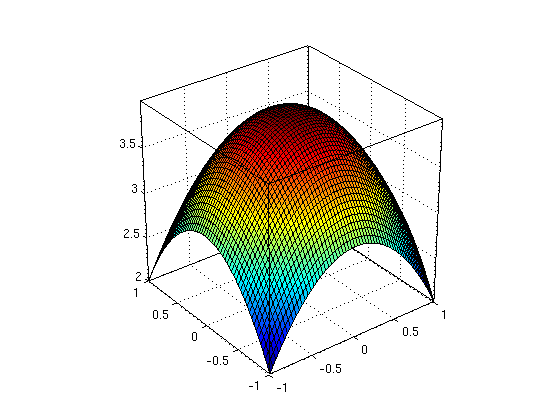
Consider the paraboloid given by z=4-x^2-y^2. Find the surface area for -1<=x<=1 and -1<=y<=1. Note that this gives difficult integrals in Cartesian coordinates.
syms x y a real f = 4-x^2-y^2 fx = diff(f,x) fy = diff(f,y) g = sqrt(1+fx^2+fy^2) % integrand for surface area I1 = int(g,y,-1,1) % inner integral over y: Matlab can do this I = int(I1,x,-1,1) % outer integral over x: Matlab cannot do this, returns int(...) Id = double(I) % use double(...) to get numerical answer ezsurf(f,[-1 1 -1 1]) nice3d
f =
- x^2 - y^2 + 4
fx =
-2*x
fy =
-2*y
g =
(4*x^2 + 4*y^2 + 1)^(1/2)
I1 =
(4*x^2 + 5)^(1/2) - ((4*x^2 + 1)*(log(4*x^2 + 1)/2 - log((4*x^2 + 5)^(1/2) + 2)))/2
I =
int((4*x^2 + 5)^(1/2) - ((4*x^2 + 1)*(log(4*x^2 + 1)/2 - log((4*x^2 + 5)^(1/2) + 2)))/2, x == -1..1)
Id =
7.4463
(2): Surface area of paraboloid
Now find the surface area of the paraboloid for (x,y) with x^2+y^2<=4. Use polar coordinates.
syms r theta real Pi = sym('pi'); X = r*cos(theta); Y = r*sin(theta); F = simplify(subs(f,{x,y},{X,Y})) % f in polar coordinates, simplify G = simplify(subs(g,{x,y},{X,Y})) % integrand in polar coordinates, simplify I1 = int(G*r,r,0,2) % inner integral, use area element r*dr*dtheta I = int(I1,theta,0,2*Pi) % outer integral ezsurfpol(F,0,2*pi,0,2); nice3d
F = 4 - r^2 G = (4*r^2 + 1)^(1/2) I1 = (17*17^(1/2))/12 - 1/12 I = (pi*(17*17^(1/2) - 1))/6