Examples: Area of parametrized surfaces
Contents
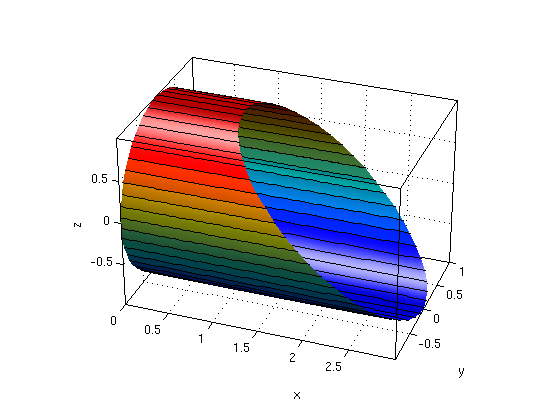
(1a) Part of cylinder
Consider the part of the cylinder y^2+z^2=1 with x>=0 and x+z<=2. Find the limits for the parameters and plot the surface.
Answer: We have y=cos(theta), z=sin(theta). Since x<=2-z and z=sin(theta) we get 0<=theta<=2*pi, 0<=x<=2-sin(theta).
syms theta x real Pi = sym('pi'); X = x; Y = cos(theta); Z = sin(theta) % parametrization of surface ezsurfpar(X,Y,Z,0,2*pi,0,2-sin(theta),theta,x) % plot surface for theta in [0,2*pi], x in [0,2-sin(theta)] nice3d; view(20,30); defaultlighting
Z = sin(theta)
(1b) Find the surface area!
R = [X,Y,Z]; Rtheta = diff(R,theta) % partial derivative w.r.t. theta Rx = diff(R,x) % partial derivative w.r.t. x N = cross(Rx,Rtheta) g = simplify(norm(N)) % surface area is given by integral of g*dx*dtheta area = int( int(g,x,0,2-sin(theta)) , theta,0,2*Pi)
Rtheta = [ 0, -sin(theta), cos(theta)] Rx = [ 1, 0, 0] N = [ 0, -cos(theta), -sin(theta)] g = 1 area = 4*pi
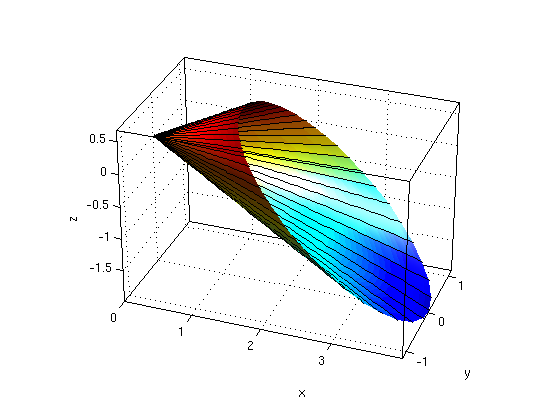
(2a) Part of cone
Consider the part of the cone sqrt(y^2+z^2)=x/2 with x>=0 and x+z<=2. Find the limits for the parameters and plot the surface.
Answer: We have y=x/2*cos(theta), z=x/2*sin(theta). Since x+z<=2 and z=x/2*sin(theta) we have x*(1+sin(theta)/2)<=2. Hence we get 0<=theta<=2*pi, 0<=x<=2/(1+sin(theta)/2).
syms theta x real Pi = sym('pi'); X = x; Y = x/2*cos(theta); Z = x/2*sin(theta) % parametrization of surface % plot surface for theta in [0,2*pi], x in [0,2/(1+sin(theta)/2)]: ezsurfpar(X,Y,Z,0,2*pi,0,2/(1+sin(theta)/2),theta,x) nice3d; view(20,30); defaultlighting
Z = (x*sin(theta))/2
(2b) Find the surface area!
Note that the outer integral is hard to do by hand.
R = [X,Y,Z]; Rtheta = diff(R,theta) % partial derivative w.r.t. theta Rx = diff(R,x) % partial derivative w.r.t. x N = cross(Rx,Rtheta) g = simplify(norm(N)) % surface area is given by integral of g*dx*dtheta area = int( int(g,x,0,2/(1+sin(theta)/2)) , theta,0,2*Pi)
Rtheta = [ 0, -(x*sin(theta))/2, (x*cos(theta))/2] Rx = [ 1, cos(theta)/2, sin(theta)/2] N = [ (x*cos(theta)^2)/4 + (x*sin(theta)^2)/4, -(x*cos(theta))/2, -(x*sin(theta))/2] g = (5^(1/2)*abs(x))/4 area = (8*pi*15^(1/2))/9