Examples from class Friday, Jan. 31
Contents
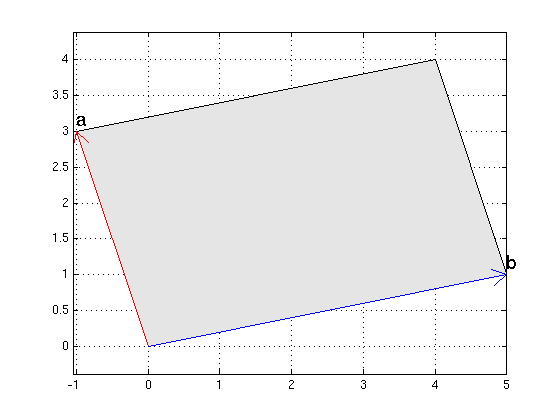
area of parallelogram in 2D
For the vectors a = (-1,3) and b = (5,1) find the area of the parallelogram using (i) the general formula, (ii) the determinant.
a = [-1,3]; b = [5,1]; Asq = dot(a,a)*dot(b,b)-dot(a,b)^2 % A^2 area1 = sqrt(Asq) determinant = det([a;b]) % note that vectors a,b have negative orientation area2 = abs(determinant) or = [0,0]; gray = [.9 .9 .9]; % RGB color gray fillpts([or;a;a+b;b],gray); hold on arrow(or,a,'r'); arrow(or,b,'b') texts(a,'a'); texts(b,'b') hold off; axis equal; grid on
Asq =
256
area1 =
16
determinant =
-16
area2 =
16
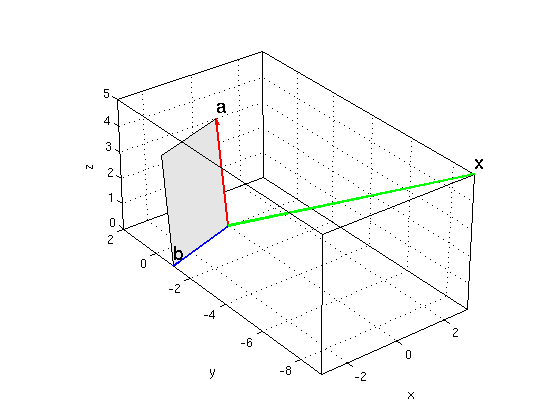
area of parallelogram in 3D
For the vectors a = (1,2,3) and b = (-3,-1,0) find the area of the parallelogram using (i) the general formula, (ii) the cross product
a = [1,2,3]; b = [-3,-1,0]; Asq = dot(a,a)*dot(b,b)-dot(a,b)^2 % A^2 area1 = sqrt(Asq) x = cross(a,b) % cross product area2 = norm(x) or = [0,0,0]; fillpts([or;a;a+b;b],gray); hold on arrow3(or,a,'r'); arrow3(or,b,'b'); arrow3(or,x,'g') texts(a,'a'); texts(b,'b'); texts(x,'x') hold off; nice3d
Asq =
115
area1 =
10.7238
x =
3 -9 5
area2 =
10.7238