Evaluating finite Fourier series using foursum
Contents
You need to download an m-file
Download the m-file foursum.m. Put it in the same folder as your other m-files.
Approximating a function using finite Fourier sums
A 1-periodic function 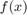 has a Fourier series
has a Fourier series
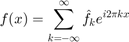
We can approximate this by computing a FINITE sum
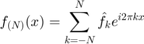
As 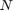 increases this should converge to the function
increases this should converge to the function 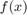 .
.
Example 1: 1-periodic function with f(x) = x on [0,1], sum over k=-10...10
Here the Fourier coefficients are
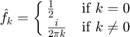
Note that the function is real-valued, and we have 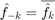 . We can therefore omit the argument fhneg of foursum, and foursum will use fhneg=conj(fhpos).
. We can therefore omit the argument fhneg of foursum, and foursum will use fhneg=conj(fhpos).
N = 10; % use frequencies up to N nv = 1:N; % vector [1,2,...,N] of frequencies fhpos = 1i./(2*pi*nv); % vector [fhat_1,...,fhat_N] for positive k x = linspace(-1,1,1000); % 1000 equidistant points from -1 to 1 for plotting plot(x,foursum(x,.5,fhpos)); grid on
Warning: Imaginary parts of complex X and/or Y arguments ignored
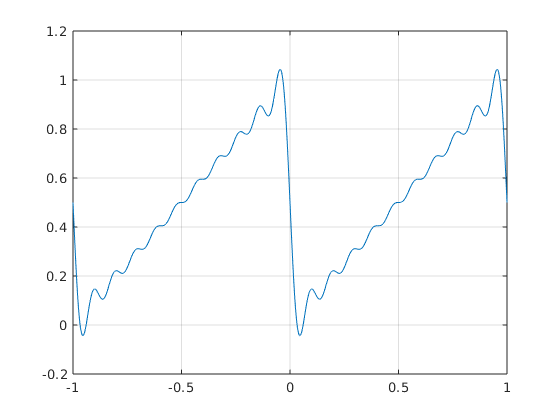
sum over k=-50...50
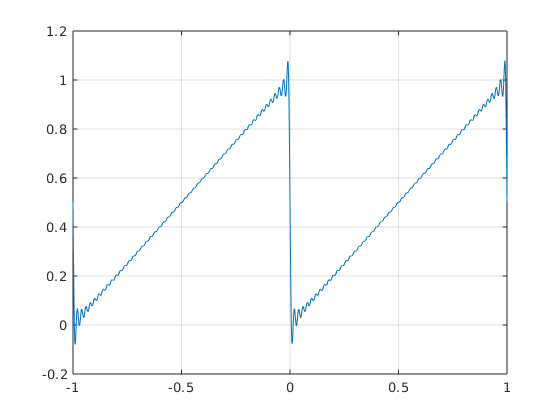
N = 50; % use frequencies up to N nv = 1:N; % vector [1,2,...,N] of frequencies fhpos = 1i./(2*pi*nv); % vector [fhat_1,...,fhat_N] for positive k x = linspace(-1,1,1000); % 1000 equidistant points from -1 to 1 for plotting plot(x,foursum(x,.5,fhpos)); grid on
Warning: Imaginary parts of complex X and/or Y arguments ignored
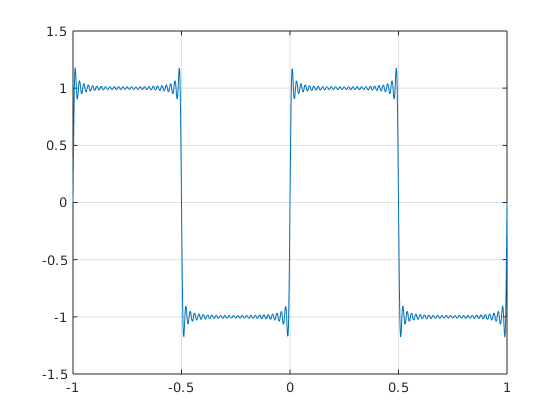
Example 2: 1-periodic function which is 1 on [0,.5) and -1 on [-.5,0), sum over k=-10...10
Here the Fourier coefficients are
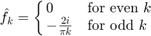
Note that the function is real-valued. Hence we have 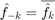 and we can therefore omit the argument fhneg of foursum.
and we can therefore omit the argument fhneg of foursum.
N = 10; % use frequencies up to N nv = 1:N; % vector [1,2,...,N] of frequencies fhpos = -2i./(pi*nv); % vector [fhat_1,...,fhat_N] for positive k fhpos(2:2:end) = 0; % set even components of fhpos to zero x = linspace(-1,1,1000); % 1000 equidistant points from -1 to 1 for plotting plot(x,foursum(x,0,fhpos)); grid on
Warning: Imaginary parts of complex X and/or Y arguments ignored
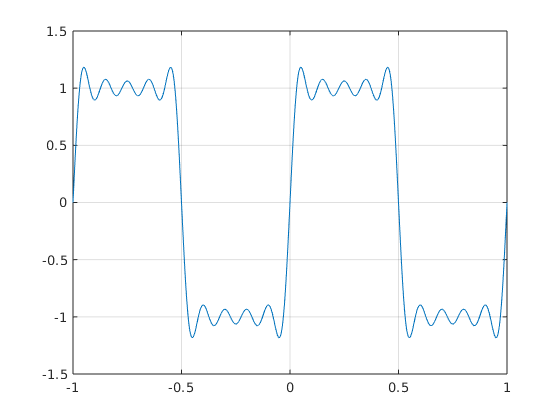
sum over k=-50...50
N = 50; % use frequencies up to N nv = 1:N; % vector [1,2,...,N] of frequencies fhpos = -2i./(pi*nv); % vector [fhat_1,...,fhat_N] for positive k fhpos(2:2:end) = 0; % set even components of fhpos to zero x = linspace(-1,1,1000); % 1000 equidistant points from -1 to 1 for plotting plot(x,foursum(x,0,fhpos)); grid on
Warning: Imaginary parts of complex X and/or Y arguments ignored